Developer Guide
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Implementation
- Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Acknowledgements
- {list here sources of all reused/adapted ideas, code, documentation, and third-party libraries – include links to the original source as well}
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
.puml files used to create diagrams in this document can be found in the diagrams folder. Refer to the PlantUML Tutorial at se-edu/guides to learn how to create and edit diagrams.
Architecture
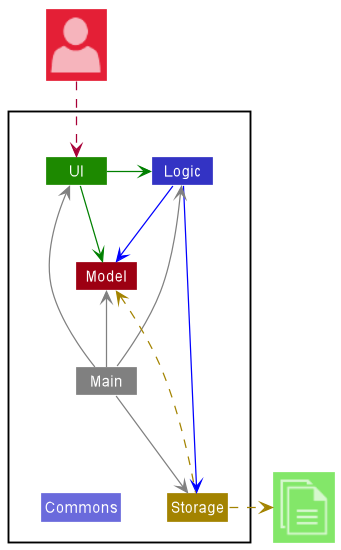
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main has two classes called Main and MainApp. It is responsible for,
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
-
UI: The UI of the App. -
Logic: The command executor. -
Model: Holds the data of the App in memory. -
Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.
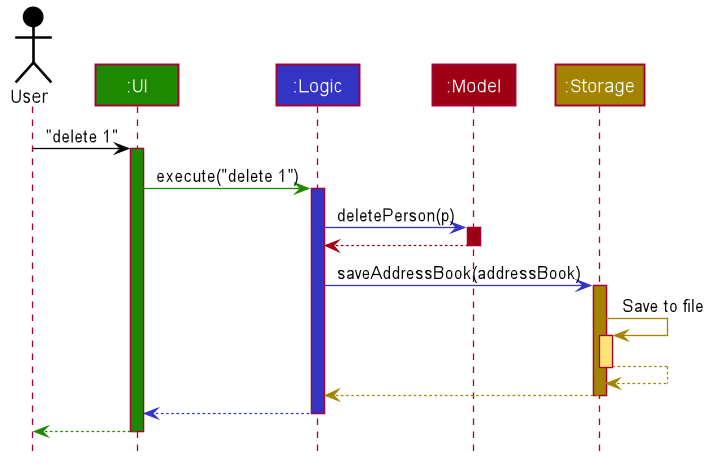
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component’s being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
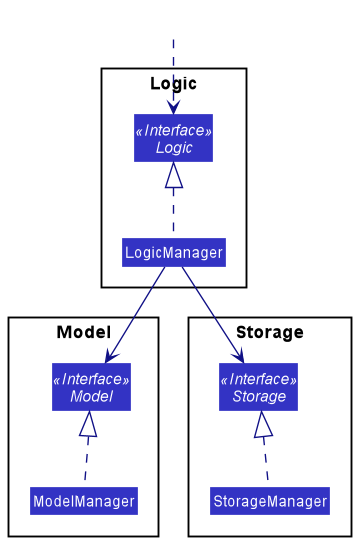
The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
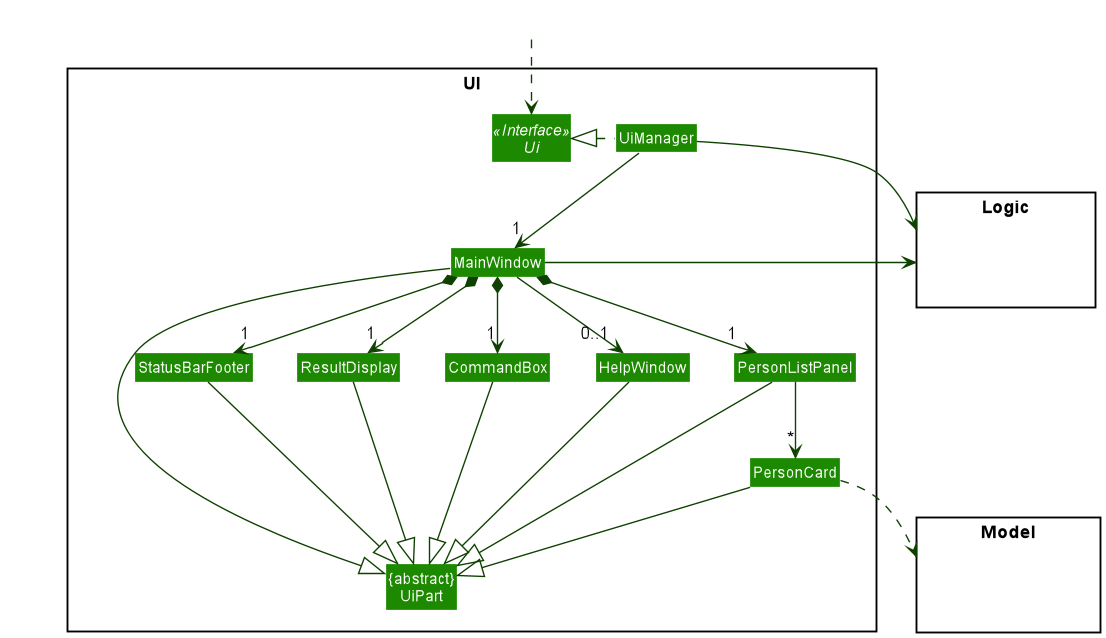
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, PersonListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysPersonobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
Here’s a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
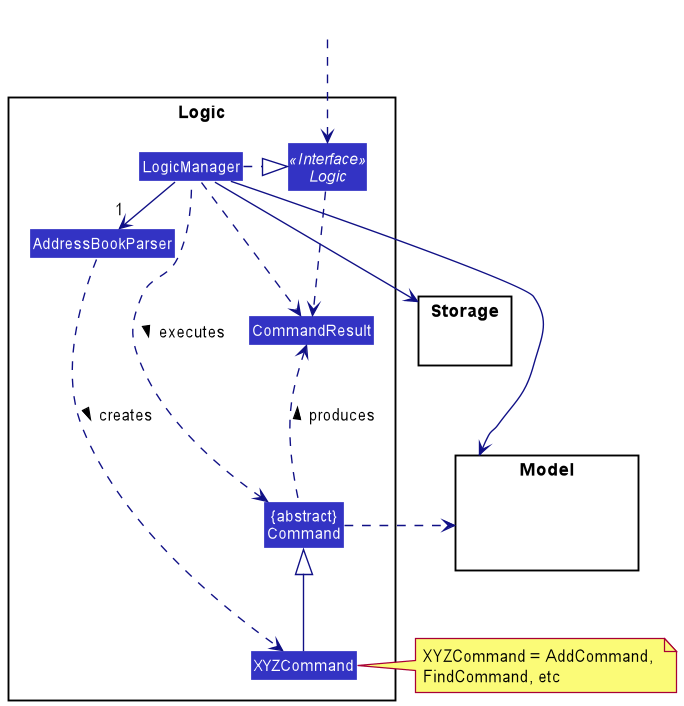
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it uses theAddressBookParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,AddCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to add a person). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
The Sequence Diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component for the execute("delete 1") API call.
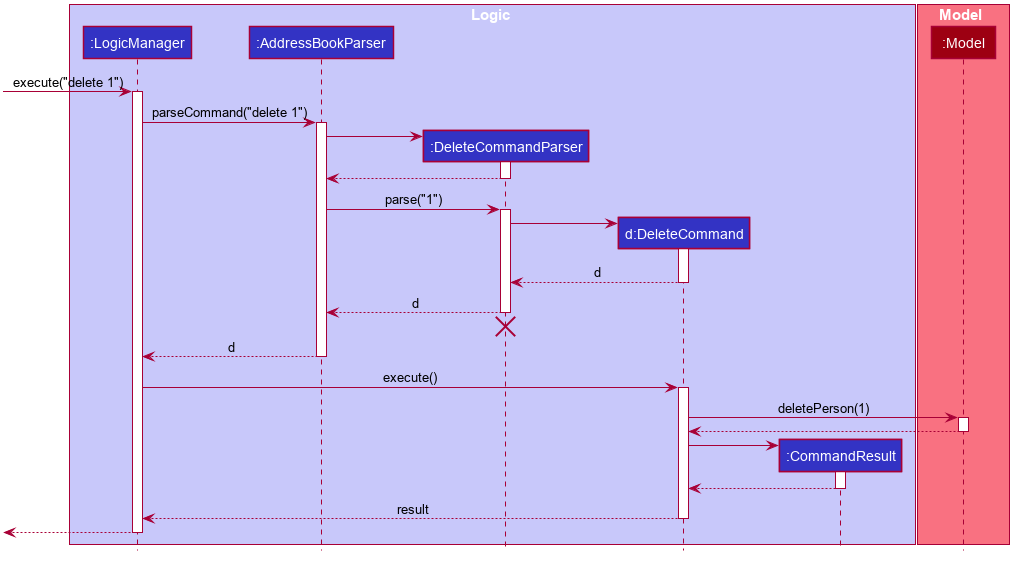
DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
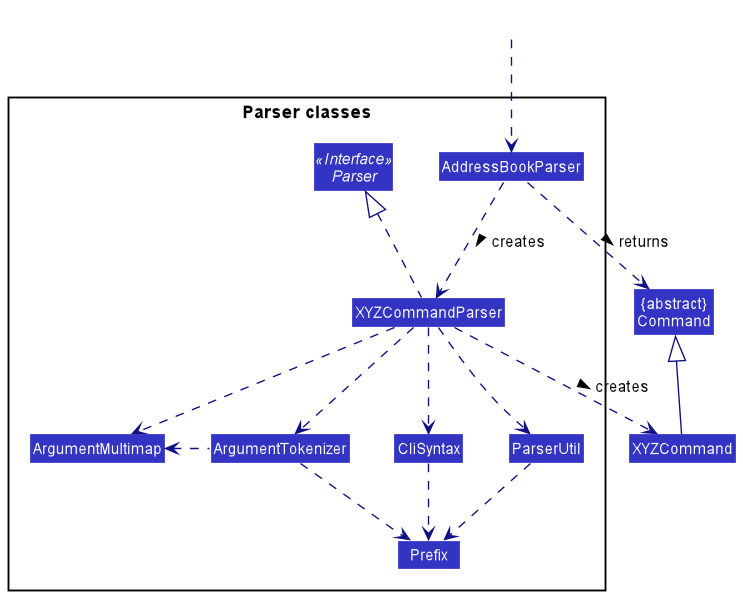
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
AddressBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theAddressBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, …) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
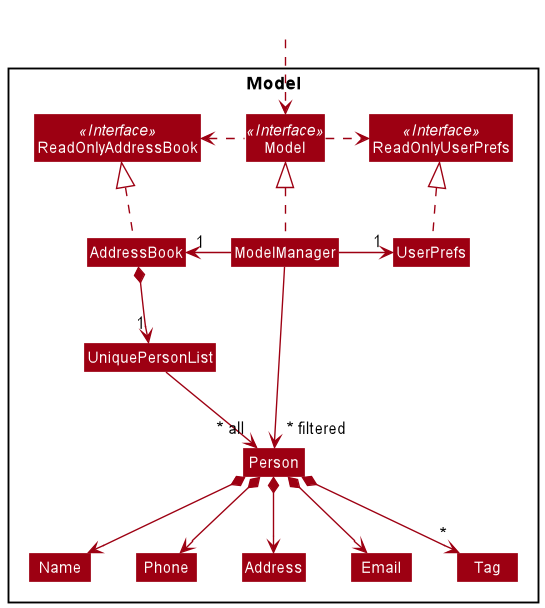
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Personobjects (which are contained in aUniquePersonListobject). - stores the currently ‘selected’
Personobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Person>that can be ‘observed’ e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
Tag list in the AddressBook, which Person references. This allows AddressBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Person needing their own Tag objects.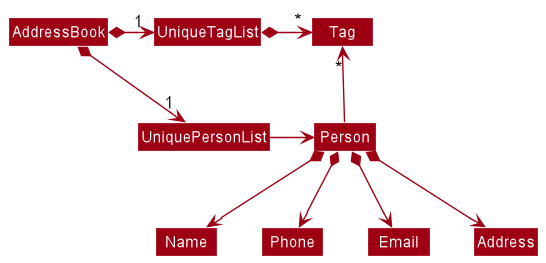
Storage component
API : Storage.java
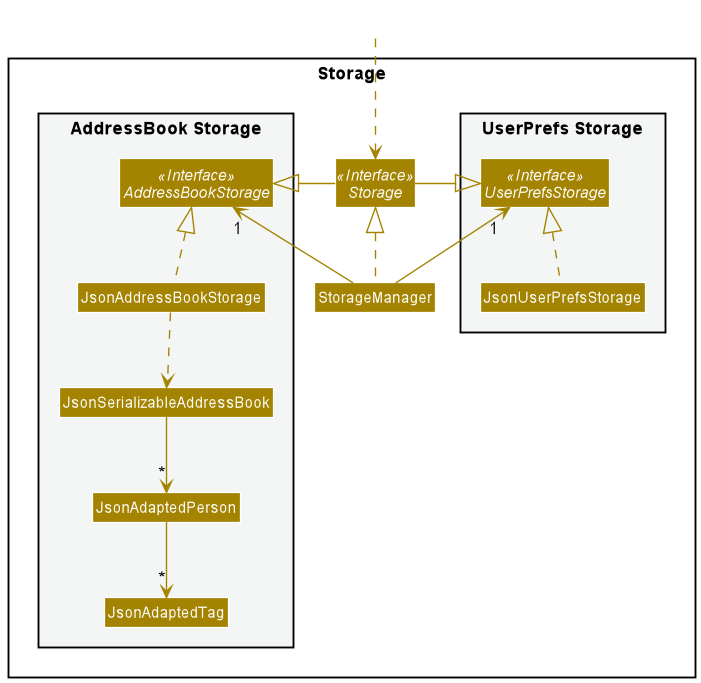
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in json format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
AddressBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent’s job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
Proposed Implementation
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedAddressBook. It extends AddressBook with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an addressBookStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
-
VersionedAddressBook#commit()— Saves the current address book state in its history. -
VersionedAddressBook#undo()— Restores the previous address book state from its history. -
VersionedAddressBook#redo()— Restores a previously undone address book state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() and Model#redoAddressBook() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
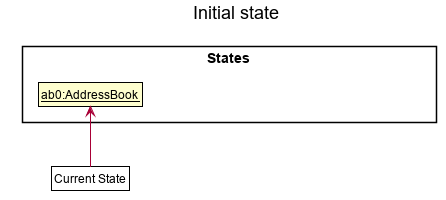
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedAddressBook will be initialized with the initial address book state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single address book state.
Step 2. The user executes delete 5 command to delete the 5th person in the address book. The delete command calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing the modified state of the address book after the delete 5 command executes to be saved in the addressBookStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted address book state.
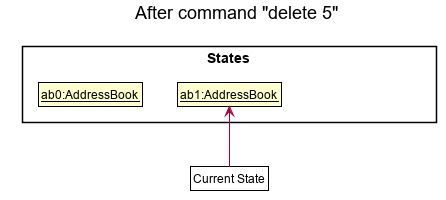
Step 3. The user executes add n/David … to add a new person. The add command also calls Model#commitAddressBook(), causing another modified address book state to be saved into the addressBookStateList.
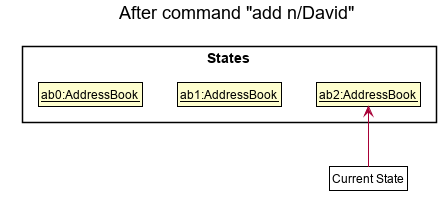
Model#commitAddressBook(), so the address book state will not be saved into the addressBookStateList.
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the person was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoAddressBook(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous address book state, and restores the address book to that state.
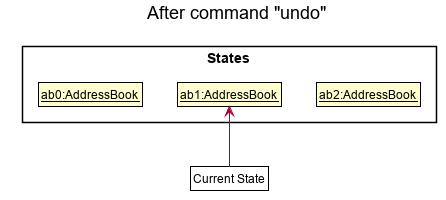
currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial AddressBook state, then there are no previous AddressBook states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather
than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how the undo operation works:
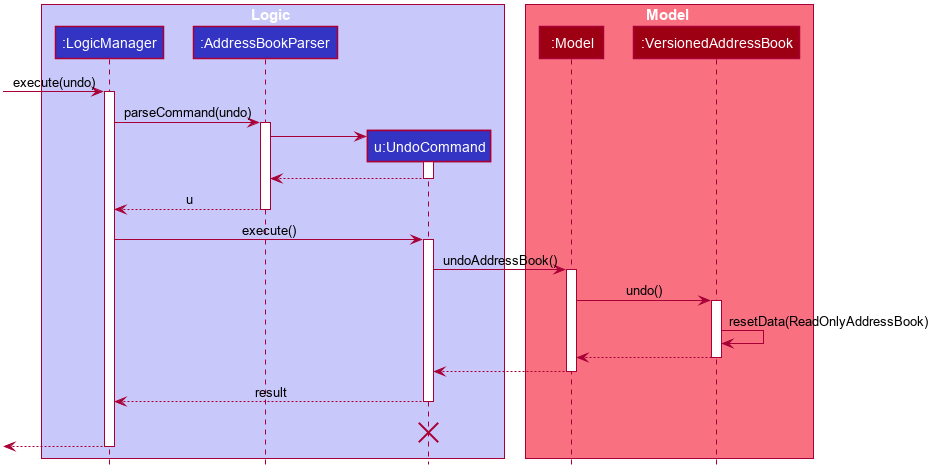
UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoAddressBook(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the address book to that state.
currentStatePointer is at index addressBookStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest address book state, then there are no undone AddressBook states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoAddressBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the address book, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitAddressBook(), Model#undoAddressBook() or Model#redoAddressBook(). Thus, the addressBookStateList remains unchanged.
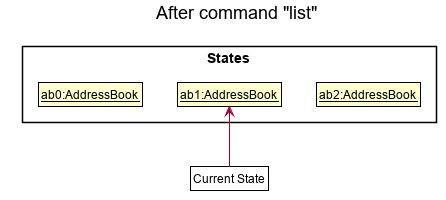
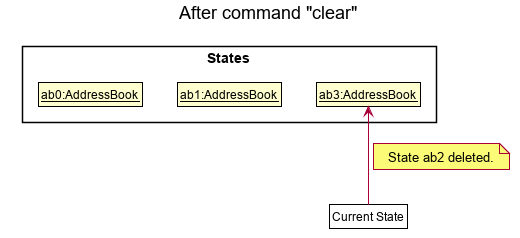
Step 6. The user executes clear, which calls Model#commitAddressBook(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the addressBookStateList, all address book states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add n/David … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
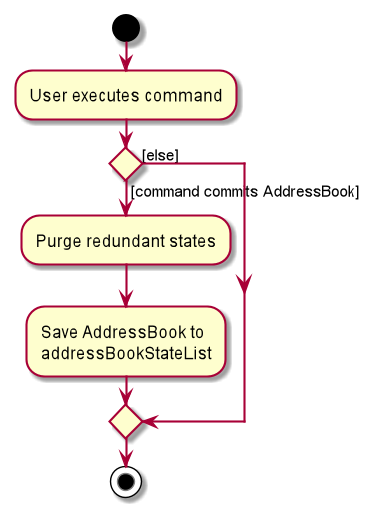
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
Design considerations:
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
-
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire address book.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
-
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by
itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the person being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
{more aspects and alternatives to be added}
[Proposed] Data archiving
{Explain here how the data archiving feature will be implemented}
Documentation, logging, testing, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
University students
- whose first language is English
- who are learning a new language
Value proposition:
- Fast way to generate flashcards to learn new languages
- Help students memorise words when learning a new language
- Gamified features such as recording of scores and tracking of improvements to make learning engaging and encourage continued usage
User stories
Categories: Usage pattern, user behaviours, general user, multiple language user, user learning style, user learning ‘rate’, level of experience, user collaboration Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | Category | As a/an… | I want to… | So that I… |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | Usage patterns | active user with hundred of cards already made | be automatically given a list of cards to test my memory | can efficiently expand my vocabulary |
| * | Usage patterns | frequent user | be able to jumble up my flashcards | am really testing my vocabulary instead of just memorising without really knowing the vocabulary |
| * | Usage patterns | forgetful user (who forgets about LingoGO!) | be reminded about using flashcards | can be actively learning new vocabularies instead of just cramming them at the last minute |
| * | Usage patterns | frequent user | be able to load up cards done x days ago | can test my memory retention of the words I learned that day |
| *** | User behaviours | lazy user | automatically generate cards by typing in the vocabulary | don’t have to spend time manually creating cards |
| * | User behaviours | user who seeks improvement | see the progress made in terms of scores | can visualize my improvement |
| * | User behaviours | organised user (who prepares flashcards based on languages) | I want to be able to combine different decks of flashcards | can prepare for my major exams (eg. mid-terms, finals) |
| * | User behaviours | mobile user | be able to access my cards wherever I am, on the go | |
| * | User behaviours | user who learns better when things are in hardcopy | have a convenient way to print out the flashcards | do not have to manually format the card design |
| * | General user | user | use the app in another language | |
| * | General user | user | see the summary statistics over a period of time | can track my progress |
| * | General user | user | be able to tag my flashcards under the categories I specify (e.g. easy, medium, for fun, nouns, etc.) | organise my flashcards easily |
| *** | General user | user | be able to add new flash cards | |
| *** | General user | user | be able to list my flashcards | |
| *** | General user | user | be able to test myself and view my performance using flashcards | |
| *** | General user | user | be able to delete my flashcards | |
| *** | General user | user | be able to update my flashcards | |
| * | Multiple language user | user who is learning multiple languages | be able to load different question sets and store my questions in different files | |
| * | Multiple language user | user who is learning multiple languages | be able to combine flashcards of the same question in different languages | can test myself in all the languages that I have learnt in one go |
| * | User learning style | auditory user | hear the vocabulary that I stored in the flashcard | can better memorize the words by sound |
| * | User learning style | visual learner | use pictures instead of words as the question part of my flashcard | can remember the vocabulary easier |
| * | User learning style | visual learner | color code my flashcards | can better memorize the words by category |
| * | User learning ‘rate’ | slow/fast learner | adjust the frequency at which the cards will be tested | can better suit my pace of learning |
| * | User learning ‘rate’ | slow learner | have cards with words I don’t remember to be shown more often to reinforce my learning | |
| * | Level of experience | long-time user | be able to delete flashcards that have not been used for over a year | only have the flashcards that are relevant to me |
| *** | Level of experience | new user | be guided through the set-up process of a flashcard | can use LingoGo! Properly |
| * | Level of experience | new user | have intuitive UI and commands | can get started easily |
| * | Level of experience | new user | have a basic set of questions available from the get go | can reduce the setup time or reduce the need for setup |
| * | Level of experience | long-time user | be able to archive my flashcards that I may not have used for a long time | can retrieve them in future should I want to use them |
| * | Level of experience | long-time user | be able to quickly search through my large library of cards easily and quickly | |
| * | Level of experience | expert user | be able to set up questions in batches | can prepare flashcards faster |
| * | Level of experience | experienced user | be able to delete multiple flashcards that are no longer relevant to me (multi-delete function) | |
| * | User collaboration | helpful user | be able to export and share my flashcards with my friends | can help them save time in generating their own set of flashcards (and they can help me too!) |
| * | User collaboration | competitive user | be able to compete with my friends based on how fast and how mnay flashcards we can get correct | will be more motivated to learn |
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is LingoGO! and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Add a flashcard
Guarantees
- A flashcard is added only if all of its information is provided.
MSS
- User requests to add a new flashcard.
- User provides information regarding the flashcard they want to add.
-
LingoGO! creates and adds a new flashcard.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. Flashcard that the user wants to add is a duplicate of a flashcard already present in LingoGO!
-
2a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 2b. Information provided by the user in incomplete.
-
2b1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: Delete a flashcard
MSS
- User requests to list out all flashcards.
- LingoGO! shows a list of flashcards.
- User requests to delete a specific flashcard from the list.
-
LingoGO! deletes the flashcard.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
-
3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Edit a flashcard
Guarantees
- A flashcard will be edited only if the edited information provided is valid.
MSS
- User requests to list out all flashcards.
- LingoGO! shows a list of flashcards.
- User requests to edit a specific flashcard from the list.
- User provides the updated information for the flashcard.
-
LingoGO! updates the flashcard with the information.
Use case ends.
Extensions
-
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
- 3a. The given index is invalid.
-
3a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 4a. The user does not provide any information.
-
4a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
- 4b. The user provides information that causes the flashcard to become a duplicate of another flashcard in LingoGO!
-
4b1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
-
Use case: Flip a flashcard
MSS
- User requests to toggle whether a flashcard’s answer can be seen.
-
LingoGO! toggles the visibility of the flashcard’s answer.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. The given index is invalid.
-
1a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: Test a user
Preconditions: Flashcard tested is not showing its answer.
MSS
- User provides an answer to a flashcard.
-
LingoGO! shows the user whether their answer is correct or not.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. The given index is invalid.
-
1a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
- 1b. The user does not provide an answer.
-
1b1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
-
Use case: Import flashcards
Guarantees
- Flashcards will only be imported if the information provided is complete.
MSS
- User creates a file containing information about flashcard questions and their corresponding answers.
- User requests to import the information in the file into LingoGO!
-
LingoGO! creates and adds new flashcards to the current list of flashcards according to the information provided in the file.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 2a. Information provided in the file is incomplete.
- 2a1. LingoGO! shows an error message.
-
2a2. User checks and edits the file to fill in any missing information.
Steps 2a1-2a2 are repeated until the data in the file is complete.
Use case resumes from step 3.
- 2b. One or more flashcards in the file are duplicates of flashcards currently in LingoGO!
-
2b1. LingoGO! shows a warning message.
Use case resumes from step 3, with LingoGO! skipping the creation and addition of the duplicate flashcards.
-
Use case: Export flashcards
MSS
- User requests to export all flashcards.
-
LingoGO! creates a file containing all information on each flashcard.
Use case ends.
Extensions
- 1a. There are no flashcards present.
-
1a1. LingoGO! shows a warning message.
Use case ends.
-
- 1b. The file name and file path is not specified.
-
1b1. LingoGO! creates a file with a default name in a default directory that will contain all information on each flashcard.
Use case ends.
-
Use case: Request for help
MSS
- User requests for help.
-
LingoGO! shows user a help message.
Use case ends.
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 flashcards without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- Should be usable to someone who has never used flashcards before.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X
- Flashcard: A memory aid that users can use to input a phrase or word in the language that they are learning along with a hidden translation
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Launch and shutdown
-
Initial launch
-
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
-
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
-
-
Saving window preferences
-
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
-
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file.
Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Deleting a person
-
Deleting a person while all persons are being shown
-
Prerequisites: List all persons using the
listcommand. Multiple persons in the list. -
Test case:
delete 1
Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Timestamp in the status bar is updated. -
Test case:
delete 0
Expected: No person is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Status bar remains the same. -
Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size)
Expected: Similar to previous.
-
-
{ more test cases … }
Saving data
-
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- {explain how to simulate a missing/corrupted file, and the expected behavior}
-
{ more test cases … }